Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Tetraodontiformes (Puffers and filefishes) >
Balistidae (Triggerfishes)
Etymology: Melichthys: Greek,melis, -itos = honey, a sweet thing + Greek, ichthys = fish (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 0 - 75 m (Ref. 9710), usually 0 - 20 m (Ref. 40849). Subtropical, preferred ?; 30°N - 29°S, 180°W - 180°E
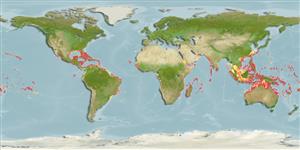
Circumtropical. Western Pacific: Ryukyu and Ogasawara islands eastward to the Tuamoto Islands. Eastern Pacific: San Diego, California, USA to Malpelo Island, Colombia (Ref. 9276). Western Atlantic: Florida, USA and Bahamas to Brazil (Ref. 7251). Reported from the Gulf of Mexico (Ref. 46995) but see Ref. 26938. Eastern Atlantic: St. Paul's Rocks (13121), St. Helena, Ascension Island, Rolas Island, and Cape Verde (Ref. 7348). São Tomé Island (Ref. 34088). Western Indian Ocean: Durban, Natal, South Africa (Ref. 4420). Uncommon in most areas but abundant around isolated oceanic islands (Ref. 9710).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 50.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5217); common length : 30.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3272)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 3;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 30-35;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 28 - 31. A dark greenish-black triggerfish with purplish overtones. Pale blue lines along bases of soft dorsal and anal fins. Scales of rear part of body have prominent keels that form longitudinal ridges (Ref. 26938).
Inhabit clear seaward reefs. More common around oceanic islands (Ref. 9276). Found on inner and outer reef crests, usually near the slope or drop-off to deeper water, where in small but loose aggregations. Sometimes swim high above substrate feeding on zooplankton (Ref. 48637). Benthopelagic (Ref. 58302). Diet consists primarily of calcareous algae and zooplankton (Ref. 1602); also feed on phytoplankton (Ref. 5213). At Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, southeast Atlantic, groups of about 100 individuals join groups of spinner dolphins to feed on feces and vomits of the cetaceans when
they congregate in a shallow bay for rest and social interactions. The postures a dolphin adopts prior to defecating or vomiting are recognized, and the fish begin to converge to the dolphin shortly before the actual voiding. Offal feeding may be regarded as a simple behavioral shift from plankton feeding to drifting offal picking (Ref. 48727). Marketed fresh (Ref. 9770).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Oviparous, distinct pairing during breeding (Ref. 205).
Matsuura, K., 2001. Balistidae. Triggerfishes. p. 3911-3928. In K.E. Carpenter and V. Niem (eds.) FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Vol. 6. Bony fishes part 4 (Labridae to Latimeriidae), estuarine crocodiles. FAO, Rome. (Ref. 9770)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquarium: commercial
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources