Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Pleuronectiformes (Flatfishes) >
Soleidae (Soles)
Etymology: Solea: Latin, solea = sandal (shoe); refered to the flat shape of the fish (Ref. 45335). More on author: Kaup.
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
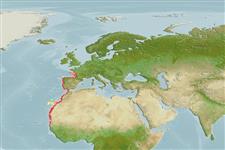
Marine; demersal; depth range 12 - 65 m (Ref. 5304). Tropical, preferred 22°C (Ref. 107945); 47°N - 14°N, 19°W - 1°W
Eastern Atlantic: Mainly Central Atlantic (from France to Angola). Western Mediterranean: Herculean migrant (entered the Mediterranean via Gibraltar) (Ref. 43448).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 60.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5304); common length : 45.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 26999)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 72-95;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 60 - 75;
Vertebrae: 44 - 46. Last ray of dorsal and anal fins joined by a low membrane to the base of the caudal fin. Supratemporal branch of lateral line forming an arch. Anterior nostril on the blind side not enlarged, its diameter about half that of the eye; it is situated rather close to the front margin of head, the distance slightly greater than that separating the nostril from the mouth cleft, 1:1-1.4. Length of scales above nasal tube on ocular side much less than the length of the tube. Gill rakers like short knobs on first gill arch on ocular side. Pectoral fin on the ocular side with a black botch over the whole middle and distal part of the fin; blind side whitish (Ref. 32649).
Flatfish with oval and asymmetric body (eyes on the right side). Interradial membrane on the pectoral fin on the eye
side is of black colour(A). This feature distinguishes it from common sole (Solea soled), which has a big black compact spot on the posterior side of this fin. In the Atlantic, from the Gulf of Biscay to the coasts of Senegal. Less frequent in the Western Meditarranean.
A predominantly littoral species. Benthonic marine species living in sandy or muddy bottoms, off coastal areas up to
100 m depth and in brackish lakes.Feeds basically on benthonic invertebrate, such as larvae from polychaets and
bivalve molluscs. Also on small crustaceans.Sexual maturity is reached when size is 30 cm. Spawning happens beween the months of March until June.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Desoutter, M., 1990. Soleidae. p. 1037-1049. In J.C. Quero, J.C. Hureau, C. Karrer, A. Post and L. Saldanha (eds.) Check-list of the fishes of the eastern tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA). JNICT, Lisbon; SEI, Paris; and UNESCO, Paris. Vol. 2. (Ref. 5304)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: experimental
More information
Common namesSynonymsMetabolismPredatorsEcotoxicologyReproductionMaturitySpawningFecundityEggsEgg development
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82805): PD
50 = 0.5020 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00851 (0.00535 - 0.01355), b=3.05 (2.91 - 3.19), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species & (Sub)family-body (Ref.
93245).
Trophic Level (Ref.
69278): 3.3 ±0.46 se; Based on food items.
Resilience (Ref.
69278): Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (Preliminary K or Fecundity.).
Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate to high vulnerability (49 of 100) .