Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Acipenseriformes (Sturgeons and paddlefishes) >
Acipenseridae (Sturgeons) > Acipenserinae
Etymology: Acipenser: Latin, acipenser = sturgeon, 1853 (Ref. 45335); medirostris: The specific name is derived from medirostris, referring to its moderate snout (Ref. 1998). More on author: Ayres.
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; freshwater; brackish; demersal; anadromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 80 m (Ref. 50610). Temperate; 10°C - 20°C (Ref. 2059), preferred 6°C (Ref. 107945); 65°N - 32°N, 166°W - 114°W (Ref. 54261)
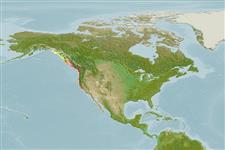
North America: Aleutian Islands and the Gulf of Alaska to Ensenada, Mexico. Considered vulnerable in Canada. The Asian population is now considered to be a separate species Acipenser mikadoi (Ref. 6866). International trade restricted (CITES II, since 1.4.98; CMS Appendix II).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 100.0, range 100 - ? cm
Max length : 270 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 96339); common length : 130 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 12193); max. published weight: 159.0 kg (Ref. 2850); max. reported age: 60 years (Ref. 72476)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 33-35;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 22 - 28. Characterized by a single row of 1 to 4 bony plates along the midventral line between the anus and the anal fin, and about 33 to 35 rays in the dorsal fin. Dorsal arises at posterior third of the total length; anal fin arises under posterior part of dorsal; pectorals originate low on the body just behind gill opening and are large and rounded; pelvic fins arise near the anus. Generally olive to dark green, lower parts more or less whitish green; a longitudinal olive-green stripe on side between lateral and ventrolateral plates, another on midventral surface; fins grayish to pale green (Ref. 27547). Barbels usually situated closer to mouth than to snout tip; coloration of scutes along side paler than skin (Ref. 86798).
Found in estuaries, lower reaches of large rivers, and in salt or brackish water off river mouths (Ref. 5723). Probably spawns in fresh water (Ref. 27547). May cover considerable distances in the ocean (Ref. 27547). Edible but with a disagreeable taste and unpleasant odor (Ref. 1998).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Page, L.M. and B.M. Burr, 1991. A field guide to freshwater fishes of North America north of Mexico. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston. 432 p. (Ref. 5723)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; gamefish: yes
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources