Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Perciformes (Perch-likes) >
Carangidae (Jacks and pompanos) > Caranginae
Etymology: Caranx: French, carangue, the name of a Caribbean fish; 1836 (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; depth range 0 - 100 m (Ref. 4233). Subtropical, preferred 24°C (Ref. 107945); 46°N - 26°S, 97°W - 32°E
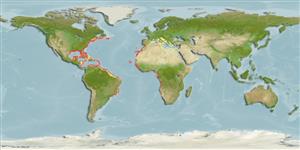
Eastern Atlantic: Senegal to Angola (Ref. 4225, 13121, 57392), including the western Mediterranean, St. Paul's Rocks (Ref. 13121), and Ascension Island. Reported from Mauritania (Ref. 55783). Western Atlantic: Nova Scotia, Canada to Brazil (Ref. 7251), including the Gulf of Mexico (Ref. 9626) and the Caribbean. Also found in Argentina (Ref. 59355). In the tropical Eastern Pacific, it is replaced by Caranx caballus Günther 1869, which may be conspecific.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 27.4 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 70.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5217); common length : 40.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5217); max. published weight: 5.1 kg (Ref. 40637); max. reported age: 11 years (Ref. 5803)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 9;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 22-25;
Anal
spines: 3;
Anal
soft rays: 19 - 21. Diagnosis: body elongate (depth comprised 3.2-3.5 times in fork length) and moderately compressed; snout slightly rounded (Ref. 57392). Maxilla ends below middle of eye (Ref. 26938, 57391). 2 dorsal fins, 1st with 8 spines, 2nd with 1 spine and 22-25 soft rays; anal fin with 2 spines, followed by 1 spine and 19-21 soft rays; anterior lobe of soft dorsal and anal fins moderately developed, their height smaller than head length; pectoral fins falcate, longer than head; scales small and cycloid; breast completely scaleless (Ref. 57391). 45 (Ref. 26938) - 56 (Ref. 57392) scutes along straight part of lateral line.
Coloration: back light olivaceous to bluish-green, sides silvery-grey to golden; juveniles with about 7 dark crossbars on sides (Ref. 57392).
A schooling species (Ref. 5217, 57391) generally not far from the coast (Ref. 5217), in coastal marine and brackish waters to at least 100 m depth (Ref. 57392). Juveniles often found in association with floating Sargassum (Ref. 5217), often entering lagoons and estuaries (Ref. 57392). Adults feed on fishes, shrimps, and other invertebrates. They spawn offshore from January through August (Ref. 26938). Eggs are pelagic (Ref. 4233). Excellent food fish (Ref. 9626); marketed fresh, frozen (Ref. 5521), and salted. Often used for bait (Ref. 26938). Maximum reported total length 550mm in Ref. 57392.
Smith-Vaniz, W.F., J.-C. Quéro and M. Desoutter, 1990. Carangidae. p. 729-755. In J.C. Quero, J.C. Hureau, C. Karrer, A. Post and L. Saldanha (eds.) Check-list of the fishes of the eastern tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA). JNICT, Lisbon; SEI, Paris; and UNESCO, Paris. Vol. 2. (Ref. 7097)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 30911)
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources