Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Perciformes (Perch-likes) >
Moronidae (Temperate basses)
Etymology: saxatilis: saxatilis=living among rocks (Ref. 79012).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
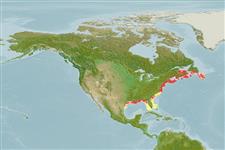
Marine; freshwater; brackish; demersal; anadromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 30 - ? m (Ref. 2850). Temperate; 8°C - 25°C (Ref. 47172), preferred 20°C (Ref. 107945); 47°N - 24°N, 94°W - 58°W
Western Atlantic: St. Lawrence River in Canada to St. John's River in northern Florida and northern Gulf of Mexico; from fresh and brackish tributaries of western Florida to Louisiana in the USA. Introduced to other countries.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 200 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 5723); common length : 120 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9988); max. published weight: 57.0 kg (Ref. 2850); max. reported age: 30 years (Ref. 1468)
Inhabit coastal waters and are commonly found in bays but may enter rivers in the spring to spawn (Ref. 2850). Some populations are landlocked (Ref. 7251). Voracious and opportunistic feeder (Ref. 5951). Larvae feed on zooplankton; juveniles take in small shrimps and other crustaceans, annelid worms, and insects (Ref. 1998, 10294); adults feed on a wide variety of fishes (alewives, herring, smelt, eels, flounders, mummichogs, rock gunnels, sand lance, silver hake and silversides (Ref. 5951)) and invertebrates (squid, crabs, sea worms and amphipods (Ref. 5951)), mainly crustaceans (Ref. 1998). Feeding ceases shortly before spawning (Ref. 1998). Utilized fresh and eaten broiled and baked (Ref. 9988).
Move into fresh or brackish water to spawn (Ref. 39467). Females spawn more than once in a season, but they don't necessarily spawn every year (Ref. 1998).
Heemstra, P.C., 1995. Moronidae. Lubinas. p. 1289-1292. In W. Fischer, F. Krupp, W. Schneider, C. Sommer, K.E. Carpenter and V. Niem (eds.) Guia FAO para Identification de Especies para lo Fines de la Pesca. Pacifico Centro-Oriental. 3 Vols. FAO, Rome. (Ref. 9320)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources