Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Myctophiformes (Lanternfishes) >
Myctophidae (Lanternfishes) > Myctophinae
Etymology: Benthosema: Greek, benthos = depth of the sea + Greek, sema, sematos = signal, flag (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
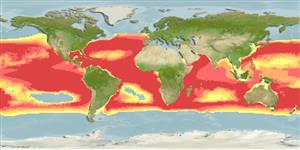
Marine; bathypelagic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 50 - 2500 m (Ref. 26165), usually 500 - 600 m (Ref. 4775). Deep-water, preferred ?; 50°N - 50°S, 180°W - 180°E
Circumglobal in tropical and temperate waters, but with a distinct equatorial gap in the Pacific (Ref. 9835). Western Atlantic: Canada to Brazil. Eastern Atlantic: Morocco to Mauritania and from Liberia to Namibia (absent in Mauritanian Upwelling Region). Indian and Pacific: confined to southern equatorial water masses, extending to 50°N and 50°S in western boundary currents. South China Sea (Ref.74511).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 2.3 range ? - ? cm
Max length : 3.9 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 4479); max. reported age: 1 years (Ref. 4882)
High-oceanic, epipelagic to mesopelagic, found in 375-750 m during the day and near the surface to 125 m at night (Ref. 4066, 58302). Adults feed on zooplankton (Ref. 9835). Caudal glands develop in both sexes from about 1.9 cm (Ref. 4775). Oviparous, with planktonic eggs and larvae (Ref. 31442).
Hulley, P.A., 1990. Myctophidae. p. 398-467. In J.C. Quero, J.C. Hureau, C. Karrer, A. Post and L. Saldanha (eds.) Check-list of the fishes of the eastern tropical Atlantic (CLOFETA). JNICT, Lisbon; SEI; Paris; and UNESCO, Paris. Vol. 1. (Ref. 4479)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
CITES (Ref. 94142)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources