Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 360 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 85726); 400.0 cm TL (female); common length : 260 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9253); max. published weight: 316.5 kg (Ref. 40637); max. reported age: 32 years (Ref. 42004)
Length at first maturity
Lm 193.0, range 180 - 230 cm
Environment
Marine; freshwater; brackish; reef-associated; amphidromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 1 - 152 m (Ref. 30573), usually 1 - 30 m (Ref. 55183)
Climate / Range
Subtropical, preferred ?; 42°N - 39°S, 117°W - 170°W (Ref. 55182)
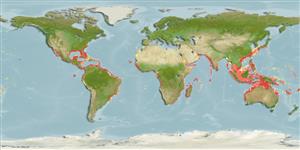
Distribution
Cosmopolitan in tropical and subtropical waters (Ref. 81283): widespread in warm oceans, rivers and lakes (Ref. 4716). Western Atlantic: Massachusetts, USA to Argentina (Ref. 58839); eastern Atlantic: Morocco, Senegal to Angola (Ref. 81283, 81623); Indo-Pacific: Kenya and South Africa to India, then, Viet Nam to Australia; southern Baja California, Mexico to Ecuador and possibly occurring in Peru. In freshwater it can be found in rivers of West Africa from Gambia River to Ogowe River (Ref. 81283).
Sympatric with Carcharhinus amboinensis, Glyphis gangeticus.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 0;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 0. Diagnosis: Carcharhinus leucas is a massive shark with a short, broad and blunt snout, small eyes and triangular saw-edged upper teeth, and lack of interdorsal ridge, characters which are sufficient to distinguish this species (Ref. 26938).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Traumatogenic (Ref. 4690)
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; gamefish: yes
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
4.3 ±0.5 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
Very Low, minimum population doubling time more than 14 years (K=0.04-0.08; tm=6-18; tmax=28)
Vulnerability
Very high vulnerability (88 of 100)
Price category