Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 76.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9015); common length : 50.5 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 12193); max. published weight: 6.8 kg (Ref. 27436); max. reported age: 3 years (Ref. 27547)
Length at first maturity
Lm 45.0, range 40 - 50 cm
Environment
Marine; freshwater; brackish; demersal; anadromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 250 m (Ref. 50550)
Climate / Range
Subtropical; ? - 21°C (Ref. 12741), preferred 3°C (Ref. 107945); 79°N - 29°N, 5°E - 114°W (Ref. 54683)
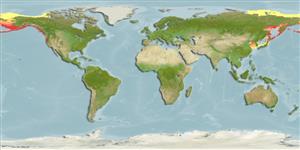
Distribution
Arctic and Pacific drainages from Mackenzie River delta, Northwest Territories, Canada to Sacramento River drainage, in California, USA; occasionally as far as La Jolla, southern California; also in northeast Asia (Ref. 5723). On Asia side, from North Korea to Jana and Lena drainages in Artic Russia. In Bering Sea north of about 40°N and from Bering Strait northeast to Point Barrow and northwest to Lena estuary (Ref. 59043). Introduced elsewhere. Occasionally hybridizes with Oncorhynchus keta producing fertile offspring (Ref. 28983).
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 10-15;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 11 - 19;
Vertebrae: 63 - 72. Distinguished by the presence of large black spots on the back and on both lobes of the caudal fin; the young have no parr marks (Ref. 27547). Body fusiform, streamlined, somewhat laterally compressed; moderately, deeper in breeding males (Ref. 1998). Mouth terminal, normally very little oblique but greatly deformed in breeding males, with lower jaw enlarged, turned up at tip, mouth unable to close (Ref. 1998). Adipose fin large; pelvic fins with axillary process (Ref. 27547). Fish in the sea are steel blue to blue-green on the back, silver on the sides and white on the belly; large oval spots present on the back, adipose fin and both lobes of the caudal fin (Ref. 27547). Breeding males become dark on the back, red with brownish green blotches on the sides; breeding females are similar but less distinctly colored (Ref. 27547). Differs from Oncorhynchus mykiss by having the following unique characters: anal fin with 11-15½ (usually 13½ ) branched rays; 177-240 scales in midlateral row; 26-33 gill rakers; large mature males with enormous hump; juveniles lacking parr marks; and lacking pink to red stripe on flank (Ref. 59043).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
4.5 ±0.4 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (tm=2; tmax=3; Fec=800)
Vulnerability
Moderate vulnerability (37 of 100)
Price category