Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 50.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 556); common length : 25.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 556); max. published weight: 1.5 kg (Ref. 556); max. reported age: 15 years (Ref. 30578)
Environment
Freshwater; benthopelagic; potamodromous (Ref. 51243)
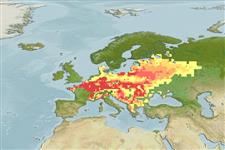
Climate / Range
Temperate, preferred ?; 56°N - 37°N, 0°E - 35°E
Distribution
Europe: Basins of Black (Danube, Dniestr, South Bug and Dniepr drainages), southern Baltic (Nieman, Odra, Vistula) and southern North Seas (westward to Meuse). Invasive or introduced in Rhône, Loire, Hérault, Seine (France) and Soca (Italy, Slovenia) drainages. Reports from the Drin drainage including Lakes Ohrid and Skadar represent a distinct species. In Appendix III of the Bern Convention (protected fauna). Asia: Turkey.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 3;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 8-10;
Anal
spines: 3;
Anal
soft rays: 9 - 11;
Vertebrae: 47 - 48. Diagnosed from congeners in Black and Caspian Sea basins by the following characters: straight mouth in individuals larger than 20 cm SL, lower lip with thick cornified sheath; dorsal fin with 9½ branched rays; anal fin with 10-11½ branched rays; scales on lateral line 52-66 (usually 60-63); eye large, diameter 50-65% of interorbital distance; and side lacking broad dark midlateral stripe. Differs from species of Chondrostoma, Protochondrostoma and Parachondrostoma in Atlantic, Adriatic and Mediterranean basins of France, Italy and Slovenia by having the following features: mouth straight, lower lip with thick cornified sheath; 27-36 gill rakers; anal fin with 10-11½ branched rays; and pectoral, pelvic, anal and caudal fins red (Ref. 59043).
(Ref. 59043). Caudal fin with 19 to 21 rays (Ref. 40476).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquarium: public aquariums
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
2.0 ±0.00 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (tm=3-4; tmax=15; Fec=10,000-40,000)
Vulnerability
Moderate to high vulnerability (48 of 100)
Price category