| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2100 |
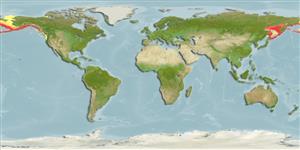
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Length at first maturity
Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; gamefish: yes; aquarium: public aquariums
Phylogenetic diversity index
(Ref. 82805)
PD50 = 0.7500 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
(Ref. 69278)
4.1 ±0.2 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
(Ref. 69278)
Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (rm=0.2; K=0.05; tm=5-20; tmax=55)