Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 60.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 35388); common length : 50.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 30578); max. published weight: 2.9 kg (Ref. 104349); max. reported age: 15 years (Ref. 3944)
Length at first maturity
Lm 24.1, range 25 - 30 cm
Environment
Marine; freshwater; brackish; demersal; pH range: 7.5 - 8.2; catadromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 1 - 100 m (Ref. 35388)
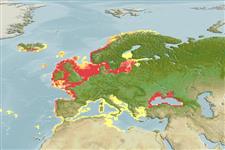
Climate / Range
Temperate; 5°C - 25°C (Ref. 13614), preferred 11°C (Ref. 107945); 72°N - 30°N, 32°W - 45°E (Ref. 54704)
Distribution
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 53-62;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 37 - 46. Flatfish, its disc width less than half its length (Ref. 3137). Small mouth (Ref. 3137, Ref. 51442). Eyes mostly (70%) on right side (Ref. 3137, 51442), 79% of dextrally oriented flounder (n = 1076) in Bos, 2000 (Ref. 57574). Rough skin, especially along the lateral line and the basis of the dorsal and anal fin (Ref. 3137). Lateral line straight, slightly rounded over pectorals (Ref. 3137). Green-olive colored (Ref. 51442), the bottom side white (Ref. 3137). Irregular reddish spots on the eye side (Ref. 35388).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: experimental; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.7500 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
3.3 ±0.2 se; Based on diet studies.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (K=0.22-0.3; tm=2-5; tmax=15; Fec= 2 million)
Vulnerability
Moderate vulnerability (42 of 100)
Price category