Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 183 cm WD male/unsexed; (Ref. 4440); max. published weight: 14.5 kg (Ref. 40637)
Length at first maturity
Lm ?, range 60 - ? cm
Environment
Marine; brackish; benthopelagic; depth range 1 - 300 m (Ref. 4440)
Climate / Range
Subtropical, preferred 26°C (Ref. 107945); 54°N - 35°S, 19°W - 36°E
Distribution
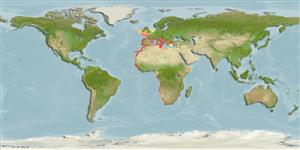
Eastern Atlantic: Madeira, Morocco and the Canary Islands north to the western coasts of Ireland and British Isles and the southwestern North Sea, south to Natal, South Africa. Also throughout the Mediterranean.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
A plain eagleray with a short, rounded snout; disc with broadly angular corners, and upper or lower jaw usually with 7 rows of plate-like teeth (Ref. 5578). Brown or blackish dorsally, white ventrally (Ref. 5578). No caudal fin (Ref. 5578).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; gamefish: yes
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5002 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
3.6 ±0.54 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Very Low, minimum population doubling time more than 14 years (Fec=3)
Vulnerability
High vulnerability (59 of 100)
Price category