Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 120 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 31730); common length : 30.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 556); max. published weight: 12.0 kg (Ref. 31730); max. reported age: 15 years (Ref. 59043)
Environment
Freshwater; benthopelagic; potamodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 10 - ? m
Climate / Range
Temperate; 10°C - 24°C (Ref. 2060), preferred ?; 57°N - 42°N, 5°W - 36°E
Distribution
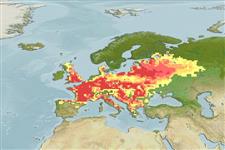
Europe: North of the Pyrénées and Alps, from Adour (France) eastward to Neman (Lithuania, Russia) drainages, in rivers draining to Atlantic, North sea and southern Baltic Sea; Danube to Dniepr drainages in northern Black Sea basin; southeastern England north to Yorkshire. Found almost throughout Mediterranean drainages of France. Locally introduced in northern and central Italy, rivers Wear, Tees and Medway and most western drainages of England.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 3 - 4;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 7-9;
Anal
spines: 2-3;
Anal
soft rays: 5 - 6;
Vertebrae: 46 - 47. Diagnosed from its congeners in France, Great Britain, Black, North, Baltic and Adriatic Sea basins and Apennine Peninsula by having the following characters: lower lip thick with a median swollen pad; tip of dorsal pointed; posterior margin of dorsal concave; last simple dorsal ray spinous, serrated along entire posterior edge; flexible segmented part of last simple dorsal ray about 20-24% of its length; fine dark spots (or no spots) in individuals larger than 10 cm SL; 53-63 total scales on lateral line; 12-14 scale rows between dorsal origin and lateral line; pelvic origin about below dorsal origin; scales with free posterior part pointed; scales on back with 1-5 well developed median longitudinal epithelial crests (Ref. 59043). Caudal fin with 19-20 rays (Ref. 2196).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquaculture: likely future use; gamefish: yes; aquarium: commercial
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
3.1 ±0.39 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (tm=3-5)
Vulnerability
High to very high vulnerability (70 of 100)
Price category