Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 16.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 188); common length : 12.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 188); max. reported age: 6 years (Ref. 3561)
Length at first maturity
Lm 10.6, range 8 - 12 cm
Environment
Marine; brackish; pelagic-neritic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 10 - 150 m (Ref. 6302)
Climate / Range
Temperate, preferred 11°C (Ref. 107945); 66°N - 30°N, 11°W - 42°E
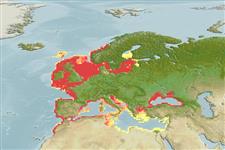
Distribution
Northeast Atlantic: North Sea and adjacent waters as far north as the Lofoten Area and the west of the British Isles, and Baltic Sea south to Morocco; also in northern Mediterranean (Gulf of Lion and the Adriatic Sea) and Black Sea.
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 13-21;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 12 - 23. Lower jaw slightly projecting, gill cover without any bony radiating striae, teeth rarely present on vomer; belly with a strong keel of scutes; last two anal fin rays not enlarged. No dark spots on flanks. Pterotic bulla absent.
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 30911)
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; bait: usually
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5312 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
3.0 ±0.07 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (rm=1.7; K=0.14-0.77; tm=1-2; tmax=6; Fec=2,000 (batch fec))
Vulnerability
Low vulnerability (25 of 100)
Price category