Classification / Names
Common names from other countries
Main reference
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 120 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 2114); common length : 50.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9137); max. published weight: 11.0 kg (Ref. 5222); max. reported age: 40 years (Ref. 74383)
Length at first maturity
Lm ?, range 50 - ? cm
Environment
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 1 - 60 m (Ref. 9710)
Climate / Range
Tropical, preferred 27°C (Ref. 107945); 29°N - 27°S, 33°E - 167°W (Ref. 5222)
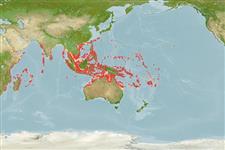
Distribution
Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and East Africa to Samoa and the Phoenix Islands, north to Japan, south to Australia. Unknown from the Persian Gulf, Hawaii, and French Polynesia. Often confused with Epinephelus polyphekadion (=Epinephelus microdon of recent authors).
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Short description
Dorsal
spines
(total): 11;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 14-15;
Anal
spines: 3;
Anal
soft rays: 8. Small juveniles (<8 cm) with small hexagonal spots on head and body becoming larger posteriorly and on vertical fins (Ref. 37816); distinguished by pale yellowish brown color with five vertical series of irregular dark brown blotches; head, body and fins with numerous close-set, small brown spots; caudal peduncle with small black saddle dorsally; cycloid scales except ctenoid in juvenile; body with auxiliary scales; moderately deep bodied, greatest depth 2.6-2.9 in SL; pelvic fins 2.1-2.4 in head length (Ref. 90102); further characterized by having head length 2.3-2.5 times in SL; flat or slightly concave interorbital area; adults dorsal head profile indented at eyes and distinctly convex from there to origin of dorsal fin; rounded preopercle, finely serrate; distinctly convex upper edge of operculum, descending almost vertically to rear end of operculum; deeply indented anterior edge of preorbital bone below nostrils; triangular posterior nostrils, 4-7 times larger than anterior nostrils in adults; maxilla extends well posterior to eye; 3-4 rows of teeth on midlateral part of lower jaw, inner teeth twice as long compared to outer teeth; canines inconspicuous; nostrils are close together (Ref. 89707).
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 4690)
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; aquaculture: commercial; aquarium: commercial
More information
ReferencesAquacultureAquaculture profileStrainsGeneticsAllele frequenciesHeritabilityDiseasesProcessingMass conversion
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates of some properties based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index
PD50 = 0.5000 many relatives (e.g. carps) 0.5 - 2.0 few relatives (e.g. lungfishes)
Trophic Level
4.1 ±0.72 se; Based on food items.
Resilience
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (K=0.16-0.20)
Vulnerability
High vulnerability (58 of 100)
Price category