Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) >
Acipenseriformes (Sturgeons and paddlefishes) >
Acipenseridae (Sturgeons) > Acipenserinae
Etymology: Huso: Latin, huso = swine (Ref. 45335).
Environment / Climate / Range
Ecology
Marine; freshwater; brackish; pelagic; anadromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 70 - 180 m. Temperate; 10°C - 20°C (Ref. 2059), preferred 16°C (Ref. 107945); 57°N - 35°N, 17°E - 60°E
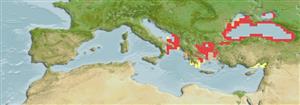
Eurasia: Caspian, Black, Azov and Adriatic Sea basins. Considered critically endangered (Ref. 59043). Appendix III of the Bern Convention (protected fauna). International trade restricted (CITES II, since 1.4.98; CMS Appendix II).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 200 - ? cm
Max length : 800 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 59043); common length : 215 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3397); max. published weight: 3.2 t (Ref. 59043); max. reported age: 118 years (Ref. 47437)
Dorsal
spines
(total): 0;
Dorsal
soft rays
(total): 62-73;
Anal
spines: 0;
Anal
soft rays: 28 - 41. Snout moderate and pointed, turning slightly upward. Lower lip not continuous, interrupted at center. Barbels oval or flat, leaf-like posteriorly, reaching almost to mouth. Five rows of scutes, dorsal 11-14 (first one smallest), lateral 41-52 on each side, ventral 9-11 on each side. Back ash-grey or greenish, flanks lighter, belly white.
Pelagic at the sea, following its prey. Undertakes upriver migration to spawn. Juveniles occur in shallow riverine habitats during their first summer. Spawns in the main course of large and deep rivers with strong current and on stone or gravel bottom (Ref. 59043). Feeds mostly on sea fishes (Black Sea whiting, anchovies, flatfishes, gobies, fry of bottom-living fishes), also crustaceans, mollusks, mysids and amphipods. Fisheries are based almost entirely on the value of the caviar, but meat also is sold fresh, smoked and frozen; eaten broiled, boiled, fried and baked (Ref. 9988). Bester, a hybrid of female Huso huso and male sterlet Acipenser ruthenus, has been successfully cultivated for its high quality eggs (Ref. 9988). The largest sturgeon and largest European freshwater fish. In Guinness Book of Records as the most expensive fish (Ref. 6472). Threatened due to overfishing for meat at the sea and for caviar in estuaries. These threats will soon cause global extinction of the natural populations. Survival can only depend on stocking (Ref. 59043).
Enters rivers from March, usually April and May (also in autumn). Survives largely by artificial propagation. About 360,000-7,700,000 eggs per female. Females carry eggs only once every five to seven years (Ref. 9988).
Kottelat, M. and J. Freyhof, 2007. Handbook of European freshwater fishes. Publications Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof, Berlin. 646 pp. (Ref. 59043)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 115185)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: commercial; aquarium: public aquariums
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources